Grit blasting is a technique that uses the impact of hard particles to produce surface patterns. High-velocity particles distort a metal surface locally by plastic deformation. The size, hardness, form, and velocity of the shot particles when using high-speed particles all have an impact on the final texture. Read More…
Our sandblast equipment is designed to handle a wide variety of applications and we use manufacturing methods that guarantee these machines will stand the test of time.

We have decades of experience in the finishing industry and we specialize in aqueous washing, abrasive blasting, vibratory finishing, polishing and buffing.

We are SurfacePrep, a trusted leader in surface preparation solutions, dedicated to delivering high-performance sandblast equipment and related products that meet the demanding needs of our customers. Our focus is on providing reliable, innovative equipment and consumables that help businesses achieve optimal surface finishes, improve efficiency, and extend the life of their tools and machinery.

At Allredi, we pride ourselves on being a leading provider of sandblast equipment, delivering exceptional solutions to meet the diverse needs of our customers. Our extensive range of products includes innovative sandblast machines, nozzles, and abrasives, all designed to enhance efficiency and performance in various applications.

At Raptor Blasting Systems, we are dedicated to designing and manufacturing high-quality sandblast equipment built to deliver exceptional performance and reliability for industrial applications. With years of expertise, we have refined our engineering processes to produce blasting cabinets, pressure systems, and abrasive recovery solutions that meet the rigorous demands of our customers.

More Grit Blaster Manufacturers
Impact from hard-shot particles can produce dimple textures, enhancing the surface characteristics of various materials. The most popular surface texturing technique is grit blasting because it creates a consistent, roughened finish with minimal effort and is simple to utilize in industrial settings. Grit blasting, also known as abrasive blasting, is widely used in surface preparation, cleaning, and finishing applications across multiple industries, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, construction, and restoration.
The strength of the pressure streams varies according to the surface type and grit being employed. This flexibility allows operators to tailor the blasting process to meet specific requirements, ranging from aggressive material removal to gentle cleaning. As a result, a task that would need hours of manual sanding may be completed in a matter of minutes, making grit blasting a highly efficient and cost-effective solution for large-scale and precision applications alike.

How Grit Blasting Works: Process, Equipment, and Media Types
Even though they are sometimes mistaken for sandblasters, grit blasting operations utilize a wide array of abrasive media to complete task-specific activities. The choice of abrasive blasting media is a critical decision in optimizing cleaning, surface preparation, or finishing results. For instance, silicon carbide, a very tough ceramic grit, is used to scrub strong surfaces like steel or cast iron, providing aggressive material removal and surface etching. Meanwhile, baking soda is a gentle abrasive that can be used on delicate materials such as aluminum or historical masonry, offering effective cleaning without damaging the substrate.
Numerous additional grit media are also employed, such as silica sand, aluminum oxide, carbide, ceramics, copper slag, glass beads, iron shot, garnet, plastic media, steel grit, walnut shells, corncob, and even fruit kernel shells. Each material brings its own properties for specific applications—ranging from rapid rust and paint removal to gentle cleaning of sensitive surfaces. These substances are broken down into a thin dust or powder with varying-sized grains by flaking, pulverizing, atomizing, or other methods, ensuring optimal impact and surface coverage during the blasting process.
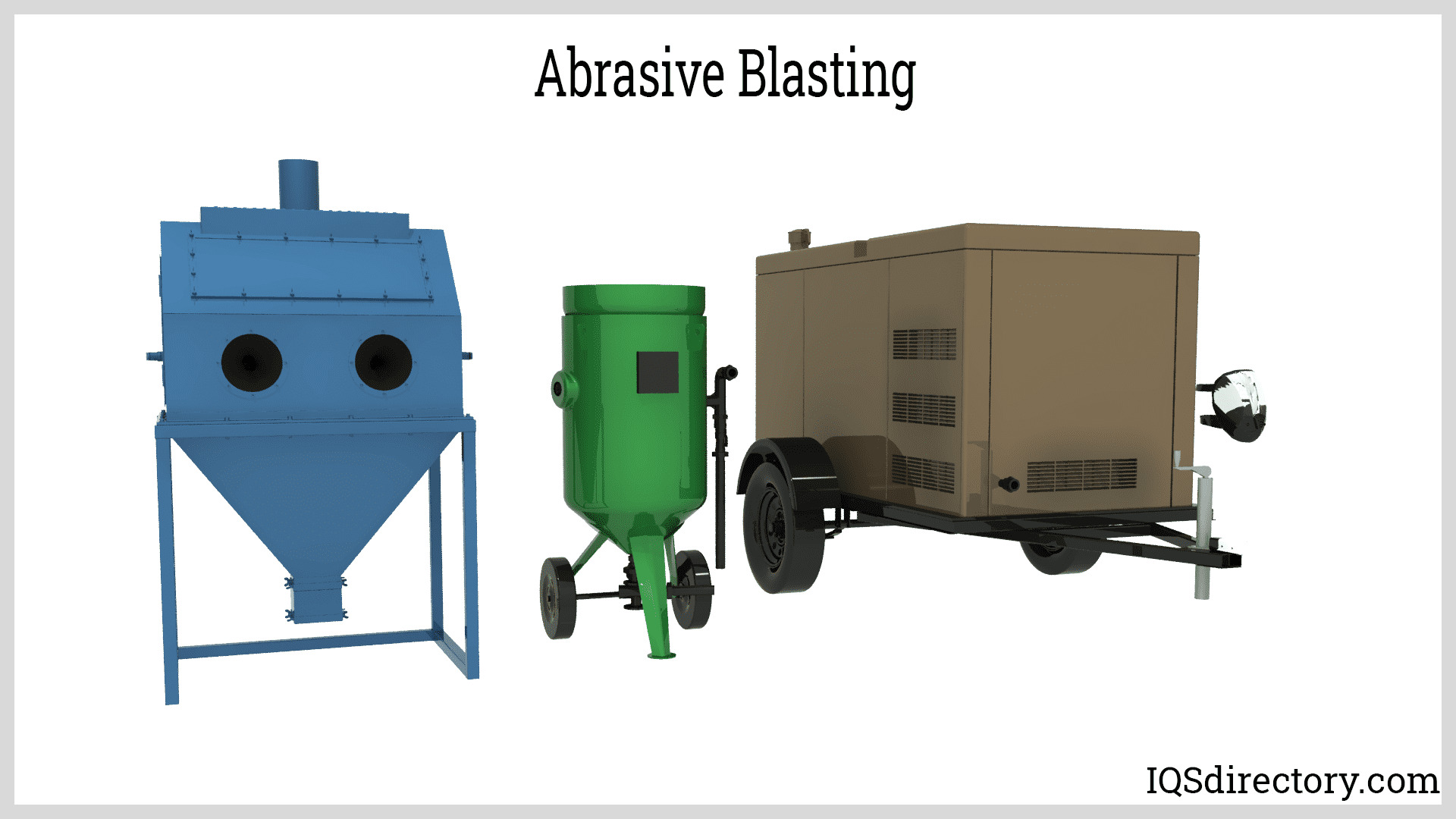
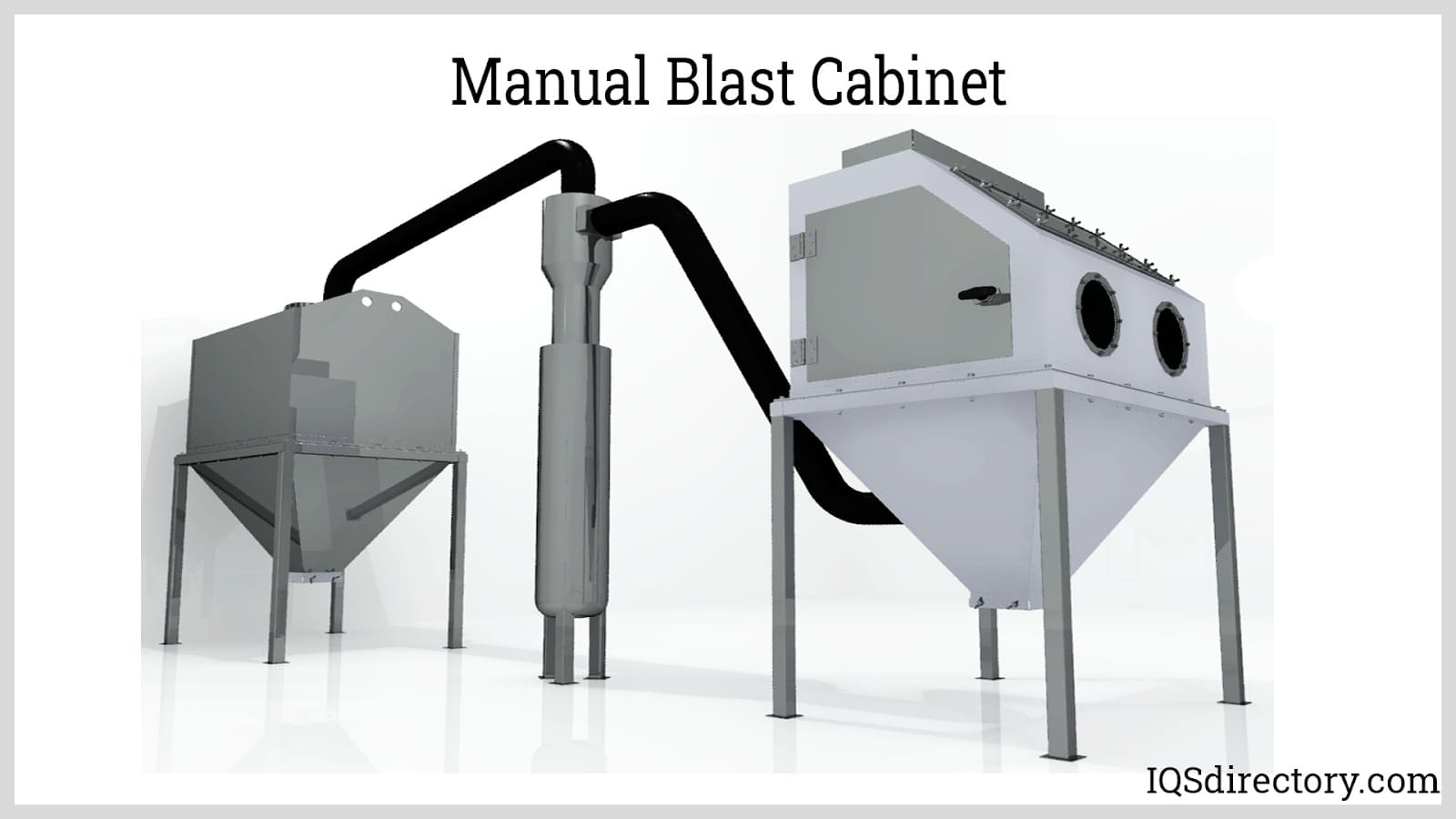
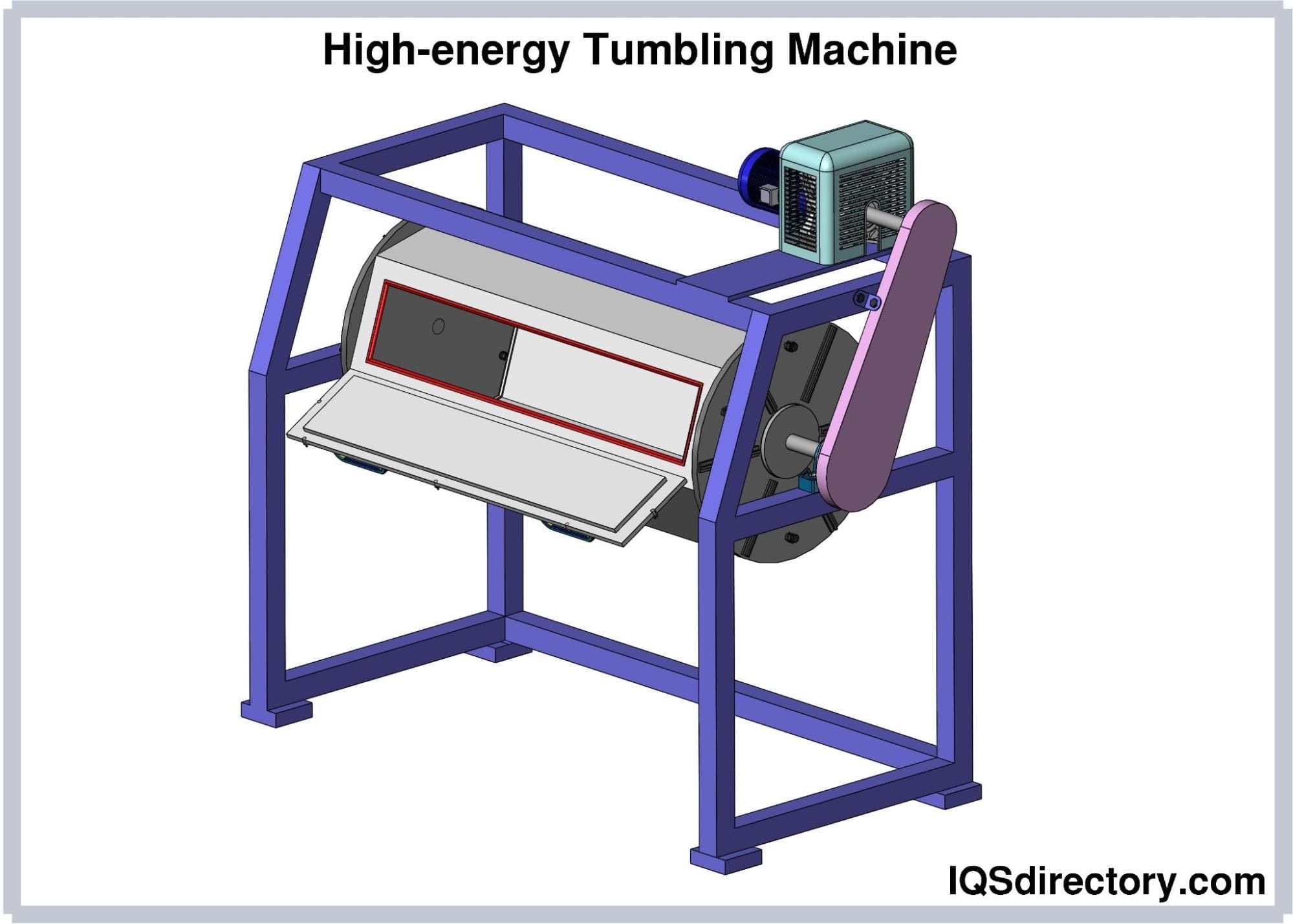
When choosing a grit blaster, the type of grit material is crucial because some machines can handle only one media type while others are designed for multi-media use. In either case, this sandblasting equipment serves the same fundamental purpose: to project abrasive particles at high velocity onto a surface, removing contaminants, coatings, corrosion, or other unwanted materials. A typical grit blasting system comprises a power source (such as compressed air or a blast wheel), a hopper or vessel containing abrasives, and a pressure generator. For applications that require media recovery and environmental control, hoses of varied lengths link the hopper to a nozzle that may be housed in a sandblast cabinet or blast room, allowing for containment and recycling of the abrasive media.

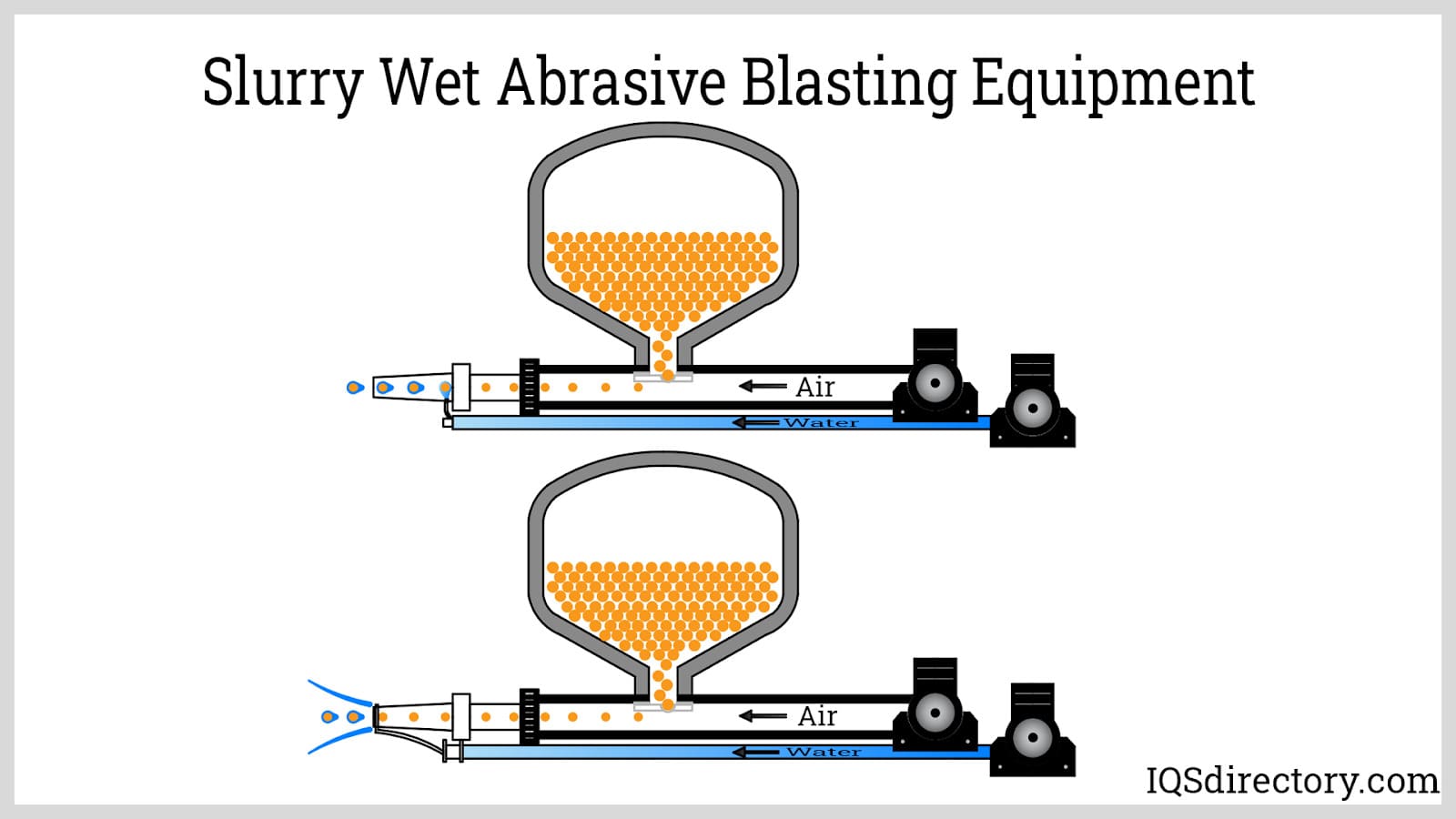
The grit blasting process starts when a trigger is pulled or a switch is pressed, creating a vacuum that forces air or, in some wet blasting systems, water through the blast gun and out the nozzle in a high-pressure stream. This stream of abrasive particles is directed towards the substrate that needs to be cleaned, resurfaced, or prepared for coating. Although this is a basic description, particular machines will differ in configuration, media compatibility, and operational features, all of which should be carefully considered in relation to the process’s intended objectives.
What Types of Grit Blasting Equipment Are Available?
Grit blasting equipment comes in a wide variety of forms to suit diverse project requirements and environments. Common types include:
- Portable grit blasters: Ideal for on-site cleaning, maintenance, and surface preparation. These mobile units are used in construction, shipyards, and field repairs.
- Blast cabinets: Enclosed systems designed for precision work and small to mid-size parts. Perfect for machine shops, automotive restoration, and manufacturing facilities.
- Blast rooms: Large enclosures for handling oversized or high-volume workpieces. Commonly found in industrial plants and aerospace manufacturing.
- Automated blasting systems: Integrated with robotics or conveyors for high-throughput, repeatable surface treatments. Used in mass production and aerospace finishing lines.
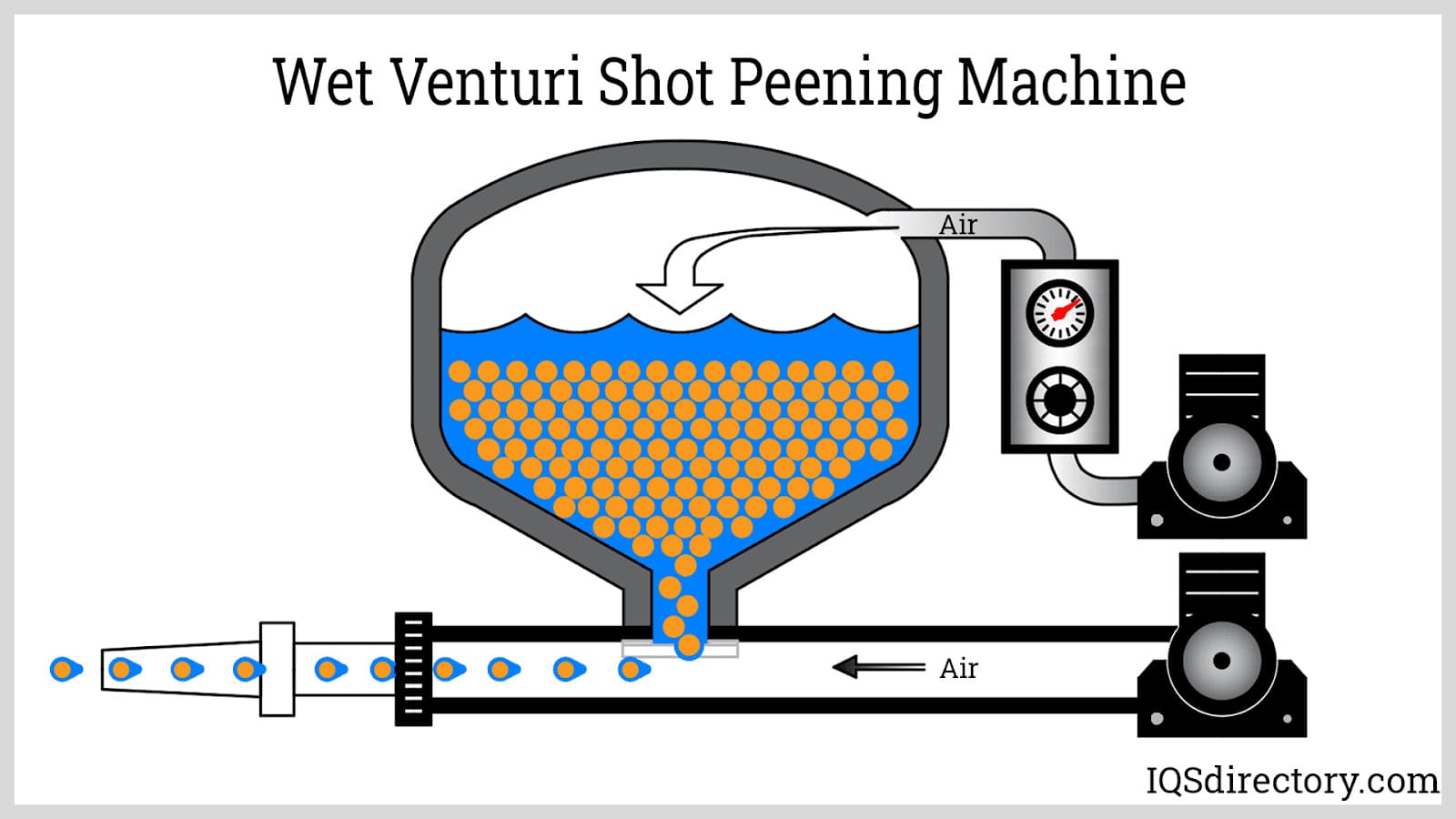
- Wet abrasive blasters: Mix water with abrasive media to reduce dust and control surface finish, making them suitable for environmentally sensitive projects.
Curious about which type suits your project best? Explore our comprehensive guide to sandblasting equipment or contact suppliers directly for personalized recommendations.
Applications of Grit Blasters: Versatile Uses Across Industries
- Surface Preparation: Grit blasters are the industry standard for preparing metal, concrete, and composite surfaces before painting, coating, welding, or bonding. By removing rust, scale, old paint, and other contaminants, blasting ensures optimal adhesion and finish quality.
- Coating Removal: Effective for stripping paint, powder coatings, adhesives, and residues from surfaces without damaging the underlying material. Essential in automotive restoration, equipment refurbishment, and infrastructure maintenance.
- Smoothing and Etching: Used to smooth rough surfaces or create a controlled profile (etching) on smooth ones, grit blasting is critical for creating anchor patterns required for certain coatings or for aesthetic finishes.
- Deburring and Deflashing: Removes sharp edges, burrs, and flash from cast, machined, or molded parts to improve safety, fit, and function, especially in manufacturing and fabrication industries.
- Peening: Shot peening, a form of abrasive blasting, is used to improve fatigue resistance and mechanical strength of metal components by inducing beneficial compressive stresses.
- Degreasing and Cleaning: Quickly cleans surfaces contaminated with oil, grease, or scale, reducing manual labor and solvent use in maintenance operations.
- Restoration and Conservation: Grit blasting delicately cleans and restores historical masonry, sculptures, and monuments, preserving their integrity while removing years of buildup.
- Glass Etching and Artistic Applications: Enables detailed etching, carving, and patterning on glass surfaces, widely used in decorative arts, signage, and architectural design.
- Wood and Plastic Surface Treatment: Prepares or textures wooden and plastic surfaces prior to painting, staining, or bonding, enhancing adhesion and visual appeal.
Looking for inspiration on how grit blasting could optimize your process? Browse our case studies and application examples to see real-world solutions in action.

Advantages of Grit Blasting: Why Choose Abrasive Blasting for Surface Preparation?
- Superior Surface Bond Strength: In relation to the aforementioned aspect, the bond for the surface after cleaning is crucial. Any fresh paint, seal, or protective coating will adhere better because blasting is a more natural process. The link between the surface and coating may not be as strong and hence may not hold up as well if chemicals are used to clean the surface.
- Enhanced Precision and Customization: It is considerably easier to make patterns with blasting than it is with other procedures since it offers a wider selection of abrasive materials and the opportunity for higher accuracy. Blasting provides the greatest choice for users wanting to be creative with the surface being cleaned.
- Eco-Friendly and Cost-Effective: There is no better alternative because the primary concept in grit and shot blasting is abrasion. Other methods would involve the use of chemicals and acids, which are more difficult to dispose of and hazardous to the environment. Grit and shot blasting produce the same effects, but there is less waste because the pellets and dust can be vacuumed up. These materials are frequently recycled. While blasting and chemicals both accomplish the same task, it's crucial to remember that chemicals have the potential to affect the surface and any newly placed coating.
- Minimized Downtime: Grit blasting is significantly faster than manual cleaning or grinding, reducing labor costs and downtime. This efficiency is especially valuable for industrial plants, shipyards, and automotive repair shops where equipment uptime is critical.
- Consistent Results: The process delivers uniform surface finishes and predictable profiles, ensuring repeatability and quality control in manufacturing and restoration projects.
- Versatility Across Materials: With the right abrasive media and equipment, grit blasting can be adapted for use on metals, glass, stone, wood, plastics, composites, and more—making it a universal solution for diverse industries.
- Health and Safety Benefits: Modern abrasive blasting systems are designed with dust extraction, containment, and operator protection in mind, minimizing workplace hazards compared to older methods or chemical-based alternatives.
- Improved Surface Lifespan: By removing corrosion, scale, and contaminants, grit blasting extends the service life of equipment, structures, and components, reducing maintenance and replacement costs over time.
Want to know if grit blasting is the right choice for your project? Review our sandblasting equipment selection guide or connect with industry experts to discuss your specific requirements.
Key Considerations When Selecting Grit Blasting Equipment and Media
Selecting the best grit blaster and abrasive media for your application involves several important decision factors. Here are some guidelines to help you choose the right solution:
- Substrate Material: The hardness and composition of the surface you’re treating will determine the appropriate abrasive media and required blast pressure. Softer surfaces require gentler media, while hard metals may need more aggressive options.
- Desired Surface Finish: Are you aiming for a smooth, polished look or a rough, etched profile? Different abrasives and nozzle types produce varying textures, so clarify your finish specifications.
- Contaminant Type: Removing paint, rust, scale, grease, or biological growths may call for different media and blasting techniques. Match your choice to the nature and thickness of the material to be removed.
- Environmental and Safety Concerns: Consider dust containment, operator protection, and local regulations regarding abrasive media disposal and air quality. Wet blasting or using recyclable media may offer compliance and safety advantages.
- Equipment Portability and Capacity: Evaluate the size of your workpieces, available workspace, and whether you need stationary, portable, or automated systems for optimal throughput and efficiency.
- Media Recyclability and Cost: Some abrasives can be reused multiple times, reducing operating costs and environmental impact. Assess the total cost of ownership, not just initial purchase price.
- Supplier Support and Service: Reliable technical support, training, and spare parts availability can make a significant difference in long-term equipment performance and ROI.
Not sure where to start? Try asking: “What’s the best abrasive media for removing rust from steel beams?” or “How do I set up a dust-free blasting system for indoor use?” Our experts are ready to help.
Industry-Specific Use Cases: Where Grit Blasting Delivers Results
- Automotive: Restores vehicle frames, wheels, and body panels by removing rust, paint, and corrosion quickly. Prepares surfaces for powder coating or painting, ensuring long-lasting finishes.
- Aerospace: Prepares aircraft components for NDT (non-destructive testing), inspection, and coating, while maintaining tight tolerances and surface integrity.
- Construction: Cleans concrete, masonry, and steel structures, removes graffiti, and prepares surfaces for waterproofing or restoration.
- Marine and Shipbuilding: Removes barnacles, scale, and marine growth from hulls and propellers. Prepares surfaces for anti-fouling coatings and repairs.
- Manufacturing: Deburrs and cleans castings, molds, dies, and machined parts, improving product consistency and performance.
- Energy Sector: Maintains turbines, pipelines, and structural steel in power plants, oil & gas, and renewable energy facilities.
- Art and Restoration: Delicately restores sculptures, monuments, and architectural details, preserving original features while removing contaminants.
Explore detailed use case studies for your industry by visiting our industry solutions page.
Frequently Asked Questions About Grit Blasting
- What is the difference between grit blasting and sandblasting?
While both processes use abrasive media propelled at high speed, “sandblasting” traditionally refers to the use of silica sand, whereas “grit blasting” encompasses a broader range of media, including steel grit, glass beads, aluminum oxide, and more. Grit blasting is generally safer for operators and the environment due to the use of non-silica alternatives. - How do I select the right abrasive media?
Consider the substrate material, type of contaminant, desired finish, and environmental factors. Consult with an experienced supplier or reference our abrasive media guide for tailored recommendations. - Can I use the same equipment for wet and dry blasting?
Some modern blasting systems are designed for both wet and dry use, offering flexibility based on your project’s dust control and surface finish requirements. Check manufacturer specifications for compatibility. - Is grit blasting environmentally friendly?
Many abrasive media options are recyclable and non-toxic. Proper containment, dust extraction, and media recycling further reduce environmental impact. Wet blasting can also minimize airborne particles. - How much does grit blasting equipment cost?
Costs range widely based on system size, features, and automation level. Portable units for small projects are relatively affordable, while industrial blast rooms and automated lines represent a larger investment. Factor in long-term operating and maintenance costs as well. - What safety precautions should I take?
Always wear appropriate PPE, use equipment in well-ventilated or contained areas, and follow manufacturer guidelines for safe operation. Regularly inspect hoses, nozzles, and pressure systems for wear or damage.
Choosing the Right Grit Blaster Supplier
To make sure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing grit blasters from a grit blaster supplier, it is important to compare at least four companies using our grit blaster directory. Each grit blaster supplier has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each grit blaster business website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple grit blaster companies with the same quote.
Ready to get started? Browse our curated list of grit blaster suppliers or request personalized recommendations based on your industry, application, and budget. Our team is here to connect you with trusted manufacturers who deliver quality, innovation, and support.
Next Steps: Maximizing Value from Your Grit Blasting Investment
- Assess your specific application requirements and consult with technical experts to match equipment and media to your needs.
- Request quotes from multiple reputable suppliers to compare features, warranties, and support services.
- Schedule equipment demonstrations or trials to confirm performance and usability in your environment.
- Review maintenance and safety documentation to ensure compliance and long-term reliability.
- Stay up to date with best practices and new technologies by subscribing to our industry newsletter and resource library.
Have questions about installation, training, or after-sales support? Contact us for expert guidance and make your next grit blasting project a success!










 Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Industrial Parts Washers
Industrial Parts Washers Sandblast Equipment
Sandblast Equipment Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services